Work-Related Musculoskeletal Injuries in Plastic Surgeons in the United States, Canada, and Norway.
Work-Related Musculoskeletal Injuries in Plastic Surgeons in the United States, Canada, and Norway.
Musculoskeletal injuries are more common among surgeons than among the general population. However, little is known about these types of injuries among plastic surgeons specifically. The authors’ goals were to evaluate the prevalence, nature, causes, and potential solutions of these musculoskeletal injuries among plastic surgeons in three different countries: the United States, Canada, and Norway.
METHODS:
A survey was e-mailed to plastic surgeons in the United States, Canada, and Norway, soliciting their demographics, practice description, history of musculoskeletal issues, potential causes of these symptoms, and proposed suggestions to address these injuries. The prevalence of various musculoskeletal symptoms was calculated, and predictors of these symptoms were evaluated using multivariate logistic regression.
RESULTS:
The survey was sent to 3314 plastic surgeons, with 865 responses (response rate, 26.1 percent); 78.3 percent of plastic surgeons had musculoskeletal symptoms, most commonly in the neck, shoulders, and lower back. U.S. surgeons were significantly more likely to have musculoskeletal symptoms than Norwegian surgeons (79.5 percent versus 69.3 percent; p < 0.05); 6.7 percent of all respondents required surgical intervention for their symptoms. The most common causative factors were long surgery duration, tissue retraction, and prolonged neck flexion. The most common solutions cited were core-strengthening exercises, stretching exercises, and frequent adjustment of table height during surgery.
CONCLUSIONS:
Plastic surgeons are at high risk for work-related musculoskeletal injuries. Ergonomic principles can be applied in the operating room to decrease the incidence and severity of those injuries, and to avoid downstream sequelae, including the need for surgery.
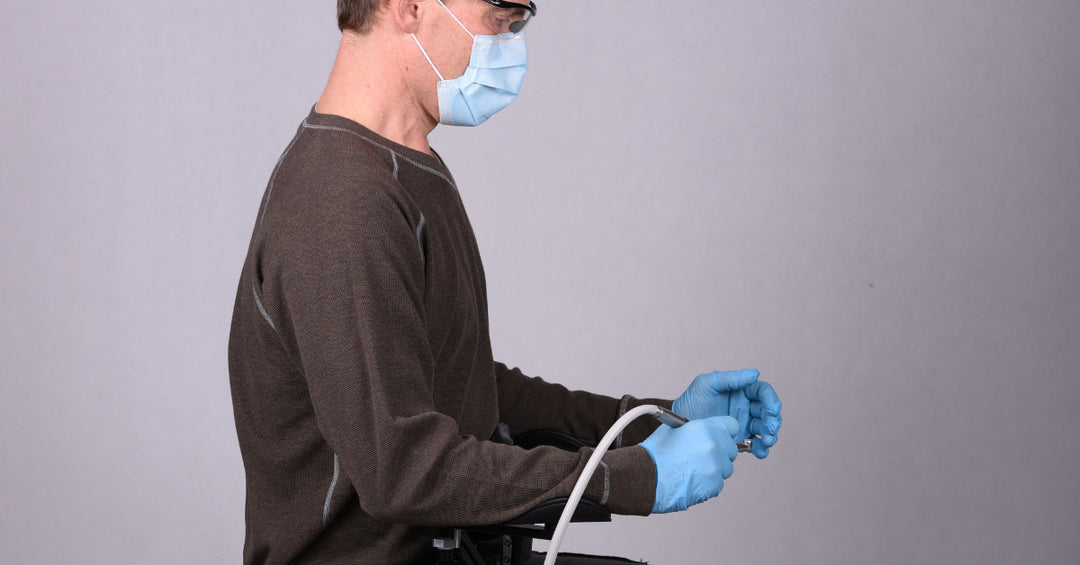
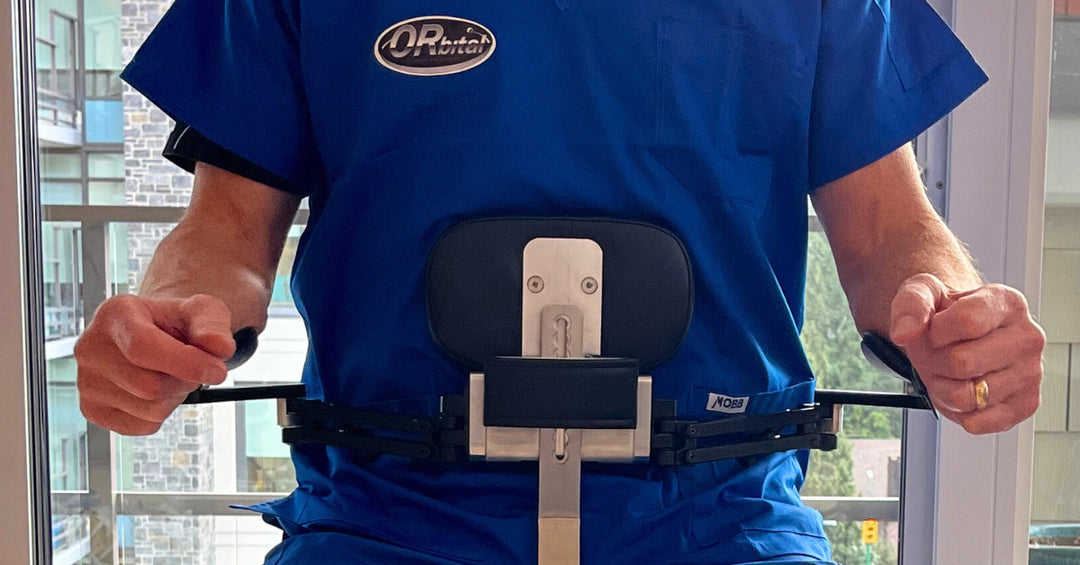
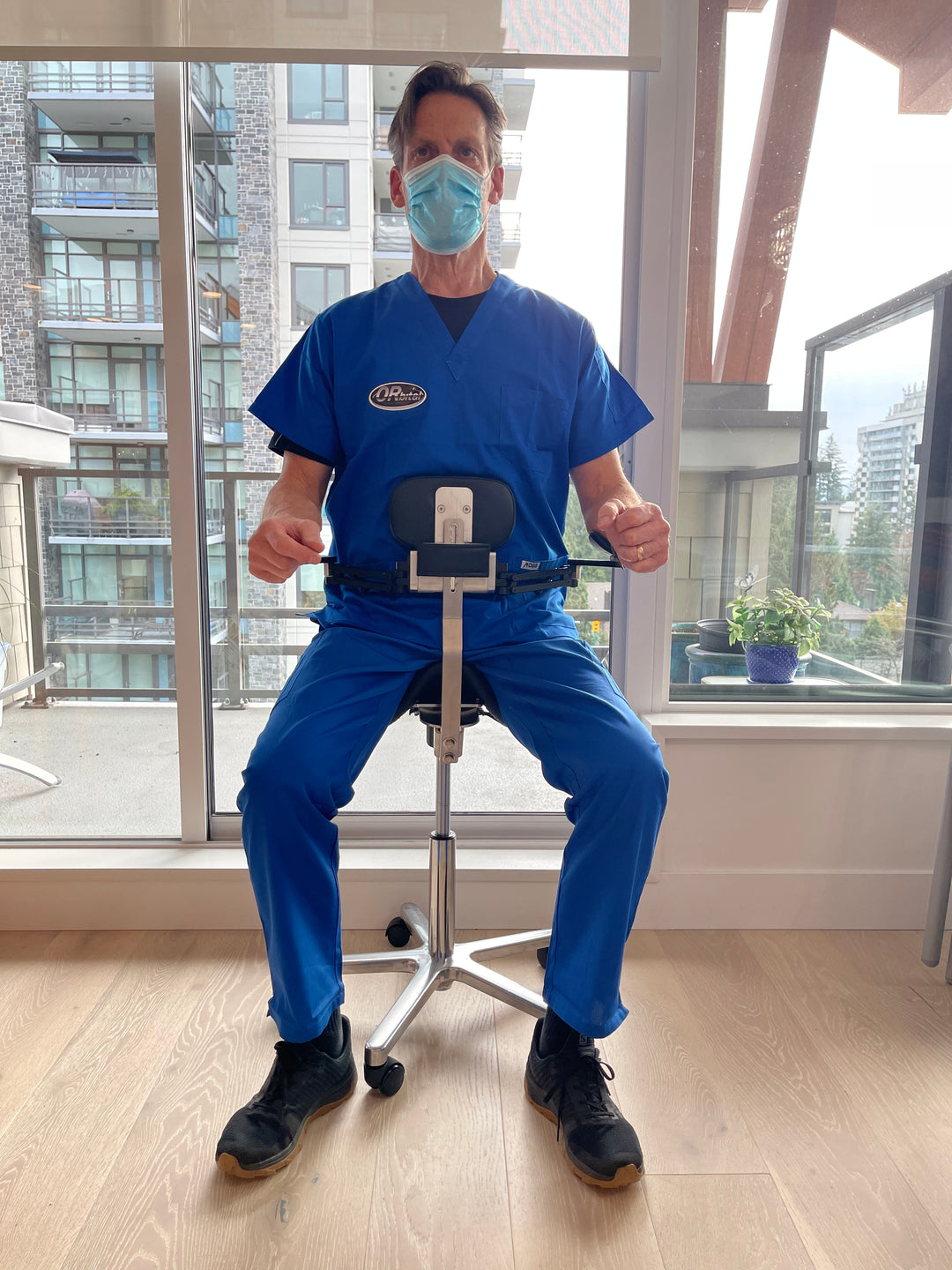
Orbital chairs were specifically designed to address these ergonomic needs. Please see our full line of medical chairs.
Full article: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29280888